The Selenium element is an essential mineral that has many vital functions. The following article discusses dietary sources with the highest levels of selenium rich foods and of protein. In the American diet, the highest contributions of selenium typically come from bread, cereals, and other grains, as well as meat, poultry, fish, and eggs. The champions of selenium content, however, are Brazil nuts, seafood, and organ meats. It’s worth noting that the selenium concentration in plant-based foods and products is highly influenced by the selenium content in the soil where the plants were grown.
The Power of Selenium
Selenium is an essential trace mineral that boosts your immune system, supports thyroid function, and defends against oxidative damage. You can learn more about selenium’s role in our health on the Dietary Guidelines website.

How much Selenium do people need?
You may be wondering how much selenium you need per day? Needs vary depending on your age and health status. For adults and children four years of age and older, the current daily recommendation is 55 micrograms per day. For pregnant and breastfeeding women, the recommendation is 70 micrograms per day.
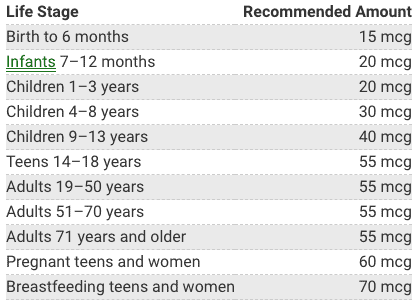
Most Americans meet recommendations for selenium intake. Selenium content in the diet varies by region, mostly due to differences in the amounts of selenium found in the soil and thus the local foods available. Animal foods tend to be the best sources of selenium — particularly meat and seafood. But lots of grain-based foods like bread, pasta, and cereal are enriched with selenium, making it easier for you to get what you need.
What if I’m not getting enough?
Selenium deficiency is fairly rare in the United States these days. You might be at a higher risk for deficiency if you: live with HIV receive dialysis have a GI condition, such as Crohn’s disease. But total selenium content of the body ranges from 13 to 30 mg, with approximately 28-46% of this stored in skeletal muscle. Plasma or serum selenium concentrations of 8 µg/dL or higher typically meets needs for selenoprotein synthesis.
If you’re not getting enough selenium in your diet, let’s explore the top 30 selenium-rich foods:
1. Brazil Nuts
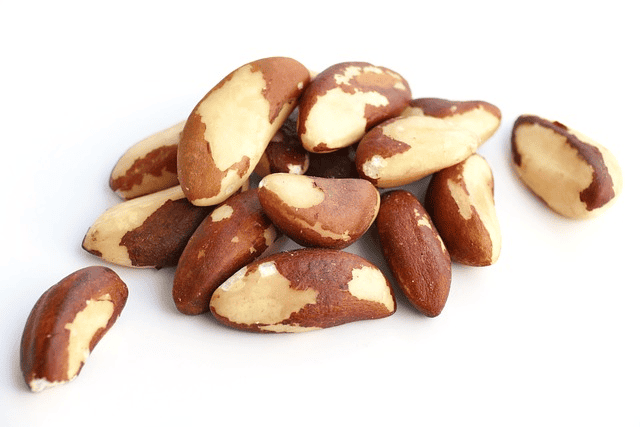

A single Brazil nut can contain anywhere between 68-91 mcg of selenium, easily surpassing the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of 55 mcg. Remember, moderation is key with Brazil nuts due to their high selenium content.
2. Oysters
Just 3 ounces of oysters provide around 38-154 mcg of selenium, making them an excellent seafood option for this essential mineral.
3. Tuna
Yellowfin tuna is particularly rich in selenium, with a 3-ounce serving offering 92 mcg, and it’s also an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids.
4. Sunflower Seeds
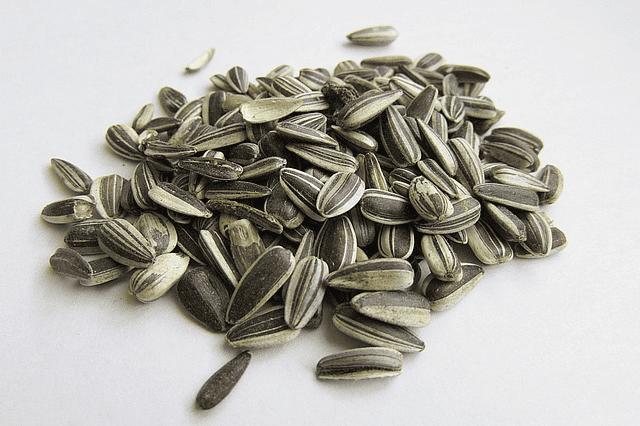

These seeds aren’t just for snacking. A quarter cup offers 34 mcg of selenium, making it a healthy, selenium-rich snack option.
5. Pork
A versatile meat, a 3-ounce serving of pork provides approximately 33 mcg of selenium. Lean cuts can be a healthy, selenium-boosting choice.
6. Beef
Whether it’s in the form of liver, steak, or roast, beef provides a good amount of selenium. For example, 3 ounces of beef liver provides around 28 mcg of selenium.
7. Chicken
Another excellent source of selenium, 3 ounces of chicken offers about 22-25 mcg. Plus, it’s a versatile protein that can be added to many dishes.
8. Rice
A cup of cooked brown rice contains around 19 mcg of selenium, making it a great side for selenium-boosting meals.
9. Turkey
Lean, protein-rich, and high in selenium – a 3-ounce serving of turkey provides about 25 mcg.
10. Cottage Cheese

One cup of cottage cheese can give you around 20 mcg of selenium. It’s also a good source of protein and calcium.
11. Eggs
A staple in many diets, one hard-boiled egg can provide 15 mcg of selenium.
12. Sardines

These small, oily fish are selenium-rich. One can provide about 45 mcg of selenium.
13. Tofu
Tofu isn’t just for vegetarians. A 3.5-ounce serving offers around 17.4 mcg of selenium.
14. Spinach
One cup of cooked spinach provides about 11 mcg of selenium, making it a nutritious, selenium-rich veggie option.
15. Milk and Yogurt
Dairy products like milk and yogurt can provide a good amount of selenium. One cup of whole milk offers 8 mcg.
16. Lentils
A cup of cooked lentils provides around 6 mcg of selenium and they’re also an excellent source of plant-based protein and fiber.
17. Bread

Whole-grain bread is a selenium source. One slice can offer around 6 mcg.
18. Oatmeal
A staple breakfast food, one cup of cooked oatmeal provides around 13 mcg of selenium.
19. Bananas
One medium banana offers about 2 mcg of selenium, a small but beneficial contribution to your daily intake.
20. Mushrooms

Depending on the variety, a cup of cooked mushrooms can provide about 5-18 mcg of selenium.
21. Salmon
Another selenium-rich fish, 3 ounces of cooked salmon provides about 40 mcg.
22. Asparagus
A cup of cooked asparagus offers about 2.8 mcg of selenium.
23. Broccoli

This green veggie isn’t just a vitamin C powerhouse; one cup of cooked broccoli provides around 2.5 mcg of selenium.
24. Garlic
While it’s not consumed in large quantities, garlic is selenium-rich. One clove offers about 1.2 mcg.
25. Cabbage
One cup of raw, chopped cabbage provides around 0.3 mcg of selenium, but it’s still a healthy veggie to include in your diet.
26. Beets

Raw or cooked, a cup of beets offers about 0.9 mcg of selenium.
27. Carrots
While they’re better known for their vitamin A content, one medium carrot also offers about 0.5 mcg of selenium.
28. Cashews
One ounce of these nuts provides about 3 mcg of selenium. They’re also a good source of healthy fats.
29. Flax Seeds
Flax seeds may be tiny, but they’re mighty. One tablespoon provides about 0.6 mcg of selenium.
30. Avocado

Avocados are primarily known for their healthy fats, but half an avocado also provides about 0.2 mcg of selenium.
Conclusion
Selenium, though a trace mineral, plays an indispensable role in maintaining optimal health. It’s crucial to include selenium-rich foods in your diet to ensure you’re meeting the daily recommended intake. Remember, a balanced diet is the cornerstone of health.
Keep in mind that while selenium is crucial for maintaining health, like all nutrients, it’s most beneficial when part of a balanced diet. If you’re considering selenium supplements, be sure to consult a healthcare provider as over-supplementation can lead to adverse effects.
The information in this blog post is intended to provide a general understanding of selenium. It should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.

